Equipment Type and Principle

Plasma Cutting Machine
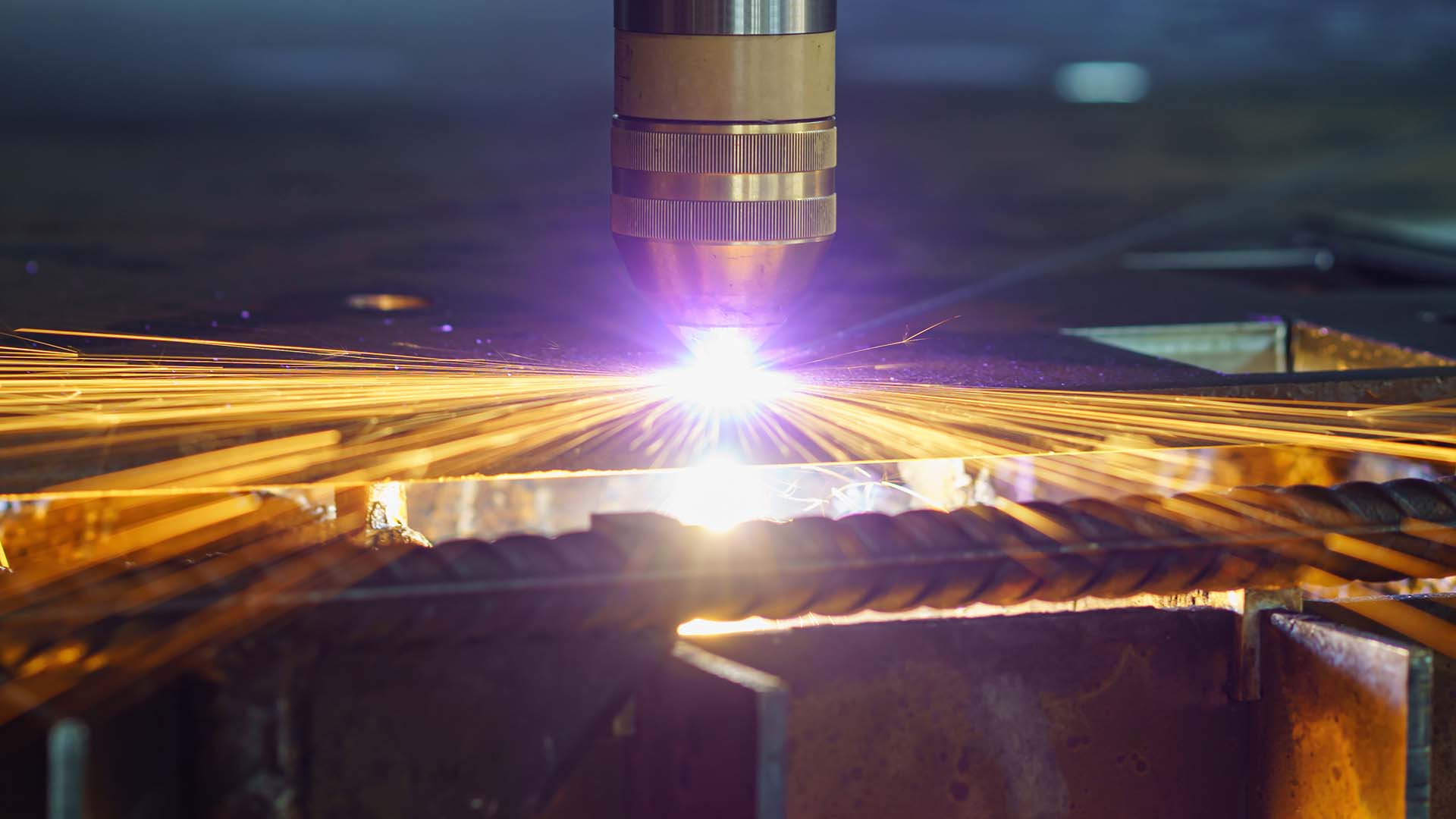
CNC plasma cutting machine is a thermal metal cutting tool that uses a high-temperature plasma gas jet to cut conductive metals. During operation, an electrode within the plasma torch excites an arc, ionizing gases such as air or nitrogen to form plasma. The high temperature locally melts the metal, and the molten slag is blown away by the gas stream. The machine precisely moves along a CAD software path via a CNC system, enabling automated straight and curved cutting. Since the plasma cutting process does not rely on flammable gases, it is safer and suitable for cutting various metals including steel, aluminum, and copper.
Fiber laser cutting machine is a device that utilizes a high-intensity beam for precise metal cutting, employing a fiber laser emitting a laser beam with a wavelength of 1064nm (^2). The laser beam is focused and irradiated onto the metal sheet, rapidly melting or vaporizing the material locally, while inert gas blows away the slag. During the cutting process, the robotic arm or gantry drives the laser head to move precisely along the CNC trajectory, enabling straight lines, curves, and irregular profile cutting. Fiber laser cutting is suitable for cutting various metal sheets and profiles, achieving clean and smooth cuts on metals such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper (^2).
Price and Return on Investment
The equipment cost of a CNC plasma cutting machine is lower, making it suitable for budget-conscious users. According to STYLECNC data, the price of an entry-level small plasma cutter is approximately $3,980 (about ¥28,000 RMB), while industrial-grade, large worktables with automation functions can cost over $20,000 (^3). In contrast, the price range for fiber laser cutting machines is much broader. Based on STYLECNC information, fiber laser cutting machines start from $14,200 (about ¥100,000 RMB) and can exceed $1,000,000 (over ¥10,000,000 RMB) (^4). Overall, plasma cutters require less investment and have lower unit equipment costs, while fiber laser cutters have higher upfront costs but offer higher unit production efficiency and superior cutting quality. In high-volume production or environments demanding high precision, laser cutters, despite their higher cost, often achieve faster ROI due to their cutting speed and lower defect rates. Conversely, for thick plate rough cutting or low-cost requirements, plasma cutters offer better cost-effectiveness.
Applicable Fields and Typical Application Scenarios
CNC plasma cutting machines are widely used in metal structural component processing and repair operations in industries such as automotive manufacturing, machinery manufacturing, shipbuilding, and construction engineering (^1). They excel at cutting thick steel plates and heavy components, commonly used for automotive chassis, steel structural components, industrial machinery parts, and pre-welding treatment. Due to their low cost and fast operation speed, manufacturing plants and cutting workshops often choose plasma equipment for high-volume sheet and tube cutting. Fiber laser cutting machines are more common in high-precision and high-value-added fields. Due to their small heat-affected zone and smooth cuts, they are widely used in sheet metal fabrication, elevator components, electronics and electrical appliances, automotive parts, and advertising signage industries (^5). These industries require high-precision processing of thin sheet metal or high cut quality; precision manufacturing plants and custom fabricators often use fiber laser equipment.
Types of Cuttable Materials and Thickness Range
In terms of material adaptability, CNC plasma cutting machines can cut almost all conductive metals, including mild steel, stainless steel, carbon steel, galvanized steel, hot-rolled steel, cast iron, copper, aluminum, bronze, titanium, and various alloys (^1). Plasma cutting is insensitive to material reflectivity and can cut highly reflective metals (e.g., copper, aluminum) and coated metals. Plasma cutting handles a wide range of plate thicknesses, typically up to several tens of millimeters depending on conditions; STYLECNC indicates common plasma cutting thickness can reach about 50mm (^6). Fiber laser cutting machines can also cut various metals, but their cutting thickness is limited by laser power. According to STYLECNC data, the high-precision sheet thickness range for fiber laser cutting is from 1mm to 200mm (^2), where low-power lasers are suitable for thin sheets (below a few millimeters), and high-power lasers (8kW, 12kW, 20kW and above) are required to cut medium-thick plates of several tens of millimeters. In summary, thin sheets (1~10mm) and high-precision requirements favor fiber laser cutting, medium-thick plates (10~50mm) can be cut by high-power fiber or plasma, while ultra-thick plates (>50mm) often rely solely on plasma or other cutting methods.
Cutting Precision, Speed, and Quality
Fiber laser cutting machines are renowned for their high precision and excellent cutting quality. STYLECNC data shows that high-power fiber laser cutters can achieve maximum cutting speeds exceeding 120 meters per minute (^2), maintaining an extremely narrow kerf with smooth, burr-free edges. The typical cutting precision of fiber laser cutters can reach ±0.02 millimeters, with a very small heat-affected zone (^2). In comparison, CNC plasma cutting machines also offer high cutting speeds (common speeds around 10,000 mm/min (^7)), but due to the less concentrated flame temperature compared to lasers, the kerf is relatively wider, and the cut edges may exhibit slight slag splatter and burrs (^8). The heat-affected zone in plasma cutting is typically larger, potentially causing deformation in heat-sensitive materials. To summarize, fiber lasers are suitable for processing requiring high surface quality and precision, delivering clean and sharp cutting results (^9); plasma cutting excels in applications prioritizing speed and thickness, where edge quality requirements are relatively less stringent.
Energy Consumption Levels
Fiber laser cutting machines have high energy efficiency, with electro-optical conversion efficiency typically exceeding 30%, resulting in relatively low energy consumption per unit cut (^10). STYLECNC notes that during fiber laser cutting, "the energy required to generate the laser is relatively small, and the electricity consumption for cutting is also less" (^11). Plasma cutting machines require high-current power supplies to sustain the plasma arc and often need external compressed air or nitrogen as auxiliary gas sources, leading to higher overall energy consumption. Overall, when processing metal of the same thickness, fiber laser cutting machines consume less electricity and auxiliary gas than plasma cutters, reducing operating costs during long-term, high-volume operations [10].
Post-Maintenance Costs and Service Convenience
CNC plasma cutting machines have a simple structure. The main consumables are electrodes and nozzles, which are low-cost and easy to replace, resulting in low maintenance costs [11]. Fiber laser cutting machines, utilizing fiber optic transmission, do not require mirrors or working gases, needing only electricity during operation [12]. STYLECNC states, "Fiber lasers do not require additional gas during operation, offering the lowest operating and maintenance costs" [13]. However, the fiber laser source itself and components like the laser cutting head are expensive. Occasional replacement of the light source or cleaning of the optical path means maintenance costs should not be overlooked. According to Eckert Cutting analysis, compared to fiber laser equipment, the initial investment and subsequent maintenance costs for plasma cutting equipment are only about one-tenth of those for fiber laser machines [14]. In conclusion, plasma machines have low consumable costs and short maintenance cycles, suitable for cost-sensitive users. Fiber laser machines, while requiring higher upfront investment, have stable structures, low failure rates, and offer more convenient daily maintenance.
Light CNC Laser Brand Introduction and Recommendation
Taking a domestic enterprise as an example, Jinan Light CNC Laser (Laifute Laser) is a well-known Chinese metal cutting equipment manufacturer. Its product line includes CNC fiber laser cutting machines and CNC plasma cutting machines [2]. Light CNC Laser’s fiber laser cutting machines use advanced fiber laser sources, capable of cutting various metal sheets from 1mm to 200mm thick, with fast speed and high precision [2]; its CNC plasma cutting machines are suitable for processing thicker metal plates, with cutting thickness up to about 50mm [6]. The company focuses on technological innovation and product quality, has extensive export experience, sells products to markets in Europe, America, and other countries, and has established a comprehensive overseas after-sales network. Light CNC Laser also provides one-stop solutions, including product customization, training guidance, and technical support, with prompt after-sales response and ample spare parts supply. When selecting cutting equipment, users can focus on domestic brands like Light CNC Laser, which have competitive advantages in cutting technology and service.
Applicable User Types and International Procurement Strategy Suggestions
- Manufacturing Plants: When large-scale production requires efficient cutting of raw plates, plasma cutters with lower costs are often chosen [3]; if the production line needs to cut complex thin sheets or requires high processing precision, fiber laser cutters can be selected [2].
- Cutting Shops (Small and Medium-sized Fabricators): Primarily undertaking various custom orders, sensitive to equipment investment. If customer orders mainly involve raw plate heavy components, economical plasma worktables can be purchased; if focusing on fine sheet metal or metal crafts, consider entry-level fiber laser machines (1.5kW~3kW) to balance precision and efficiency.
- End-Users (Workshops, Maintenance Units): Require flexible and versatile equipment. Plasma machines, being cheap and easy to maintain, suit individuals or small workshops for metal part cutting; fiber laser machines suit hobbyists or small-batch producers, users often focusing on automation and cutting quality, and should choose lower-power but high-quality laser models.
- International Buyers: When promoting in overseas markets, consider shipping costs, tariffs, and labor levels in the target market. Generally, price-sensitive regions (e.g., developing countries) can focus on promoting low-cost plasma equipment; markets with high demands for precision and automation (e.g., developed countries in Europe and America) may opt for higher-end fiber laser equipment. Local voltage compatibility and after-sales network coverage should also be considered during selection.
- Agents/Brand Owners: As distributors with proprietary brands, focus on the overall performance and customer experience of the product. Consider partnering with reputable brands or manufacturers with strong export capabilities, such as establishing cooperation with manufacturers like Light CNC Laser. Agents should provide customized solutions for different customer segments, e.g., offering high-power plasma solutions for the petrochemical industry and recommending fiber laser solutions for the electronics manufacturing industry, while ensuring good after-sales service and technical training.
Procurement Strategy Suggestions for International Importers or New Brands Entering the Chinese Market: It is recommended that importers and new brands, after researching market demand, collaborate with experienced local manufacturers or agents. On one hand, reliable Chinese manufacturers with comprehensive after-sales service (like Light CNC Laser) can be chosen as suppliers, leveraging their understanding of the local market and service network. On the other hand, emphasis should be placed on product certification and user feedback, actively customizing products and services. For new brands, entering the Chinese market requires certain localization capabilities, such as establishing local technical support teams and providing timely maintenance services to increase customer trust. In conclusion, when selecting CNC cutting equipment, comprehensively consider the characteristics of the cutting task, procurement cost, production capacity needs, and post-purchase service capabilities to make the optimal decision. [2] [6]
References: STYLECNC data compiled equipment information and industry insights [2] [6] [4] [9] [8] [12] [11] (The above content is based on the latest product information and market conditions).
1 3 6 7 CNC Plasma Cutter – STYLECNC
https://www.stylecnc.cn/plasma-cutter/
2 4 5 12 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine – STYLECNC
https://www.stylecnc.cn/fiber-laser-cutting-machine/
8 9 10 Laser Cutting vs Plasma Cutting: A Detailed Guide | RapidDirect
https://www.rapiddirect.com/blog/laser-cutting-vs-plasma-cutting/
11 cnc plasma cutting machines cnc laser cutting machines – Eckert
https://eckert-cutting.com/knowledge-base/plasma-vs-fiber-laser-advantages-disadvantages-estimated-costs.html